Innodb系统表-结构解析
MySQL中在information_schema下, 有几张’INNODB_SYS%’命名的系统表,其中记录了当前实例下Inoodb存储的表和索引等信息,也称之为数据字典,这些内容存储在ibdata1系统表空间文件中。在某些情况下,没有了.frm文件,也可以读取ibdata1文件获取对应的表结构。本文即介绍一下系统表空间结构及如何读取ibdata文件。
[TOC]
基本文件结构介绍
数据页组成及类型
数据文件和系统文件都是由多个数据页组成,每个数据页16K(默认),每个数据页都有不同的作用,有以下几种类型(storage/innobase/include/fil0fil.h):
1 | /** File page types (values of FIL_PAGE_TYPE) @{ */ |
每个数据页头部有38自己的 FIL Header , 结构内容:
| 大小(字节) | 字段 |
|---|---|
| 4 | Checksum |
| 4 | Previous Page |
| 4 | Next Page |
| 8 | LSN for last page modification |
| 2 | Page Type |
| 8 | Flush LSN |
| 4 | Space ID |
解析FIL Header可以得到一些有用内容:
offset //相对文件的偏移量
previous/next page //当前页面前后节点的偏移量, 构成链表
page type //page的类型,对应上面所述
space id //表空间ID
ibdata1文件结构
ibdata1文件是系统表空间,space id为0 , 结构如下:
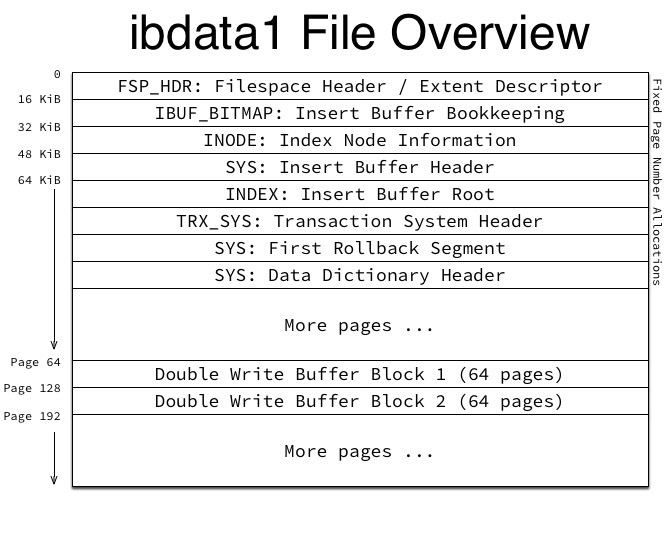
从上图中看到,ibdata1文件中的第7个页面,为FIL_PAGE_TYPE_SYS类型数据页,存放 Data Dictionary Header ,这个页面中存储内容对应的偏移量如下(storage/innobase/include/dict0boot.h):
1 | /* The offset of the dictionary header on the page */ |
其中DICT_HDR_TABLES、DICT_HDR_TABLE_IDS、DICT_HDR_COLUMNS、DICT_HDR_INDEXES、DICT_HDR_FIELDS就分别对应INNODB_SYS_%这几个系统表聚集索引(DICT_HDR_TABLE_IDS是SYS_TABLES的二级索引page)。解析这几个page就可以得到对应系统表中的数据。
hexdump -C ibdata1 解析
从0开始的第7个page偏移量大小是1c000,从这里开始经过(FSEG_PAGE_DATA+ DICT_HDR_TABLES) 70字节,之后开始读取的内容即为这几个系统表对应的page号:
DICT_HDR_TABLES // 8
DICT_HDR_TABLE_IDS // 9
DICT_HDR_COLUMNS // 10
DICT_HDR_INDEXES // 11
DICT_HDR_FIELDS // 12
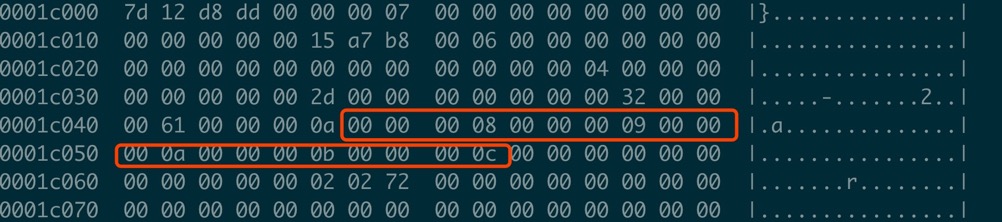
数据页解析
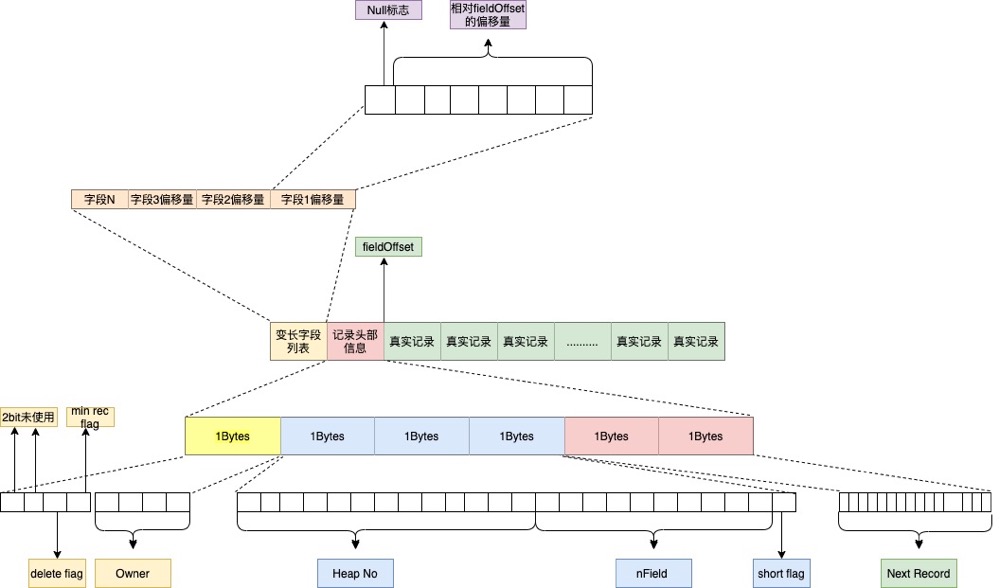
DICT_HDR_%对应的数据页类型为INDEX类型,INDEX结构如下:
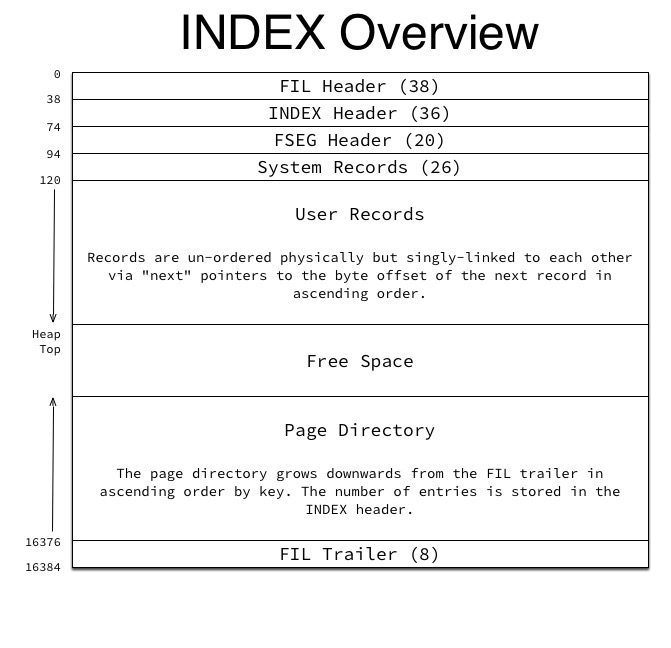
其中INDEX Header 结构如下:
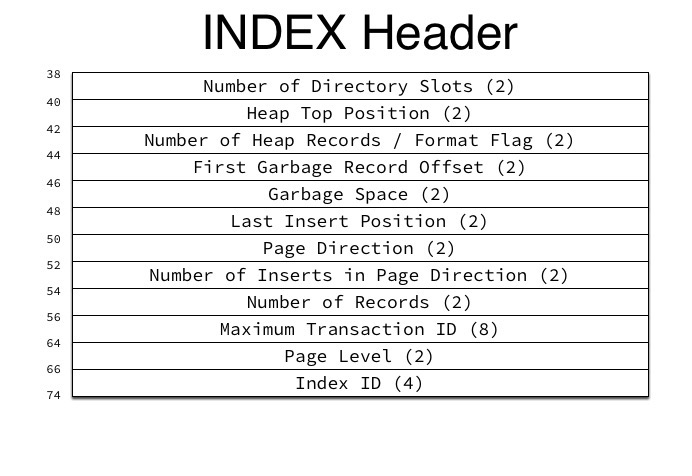
上面这两张图中Nmuber of Directory Slots和Page Directory比较重要,Slots的作用是加快在页面内数据的查找速度,实现二分查找,通过解析Nmuber of Directory Slots可以得到page中总共有多少Slot,每个Slot为2个字节,存放相对于page的偏移量。
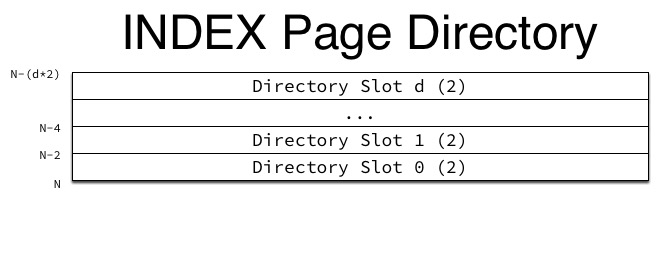
page从后向前读取Directory Slot 中的偏移量,实现二分查找,加快在页面中查找数据的速度 ,组成结构如下:
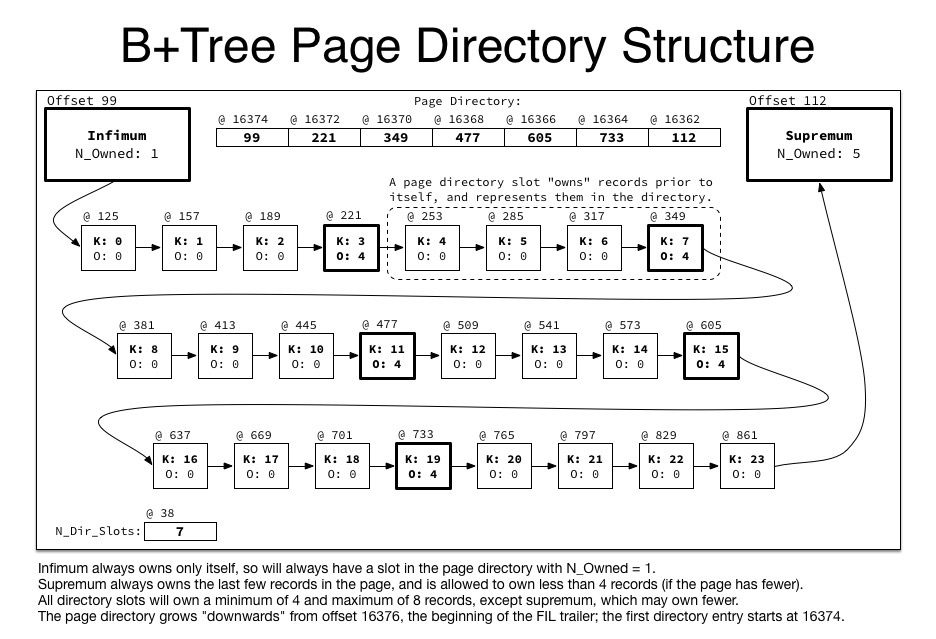
例如上图中总共有7个Slot, 存放的偏移量数据为[99, 221, 349, 477, 605, 733, 112], 如果要查询K=10这条记录,只需要扫描[477,349]这两个偏移量对应的Slot即可找到对应的数据。每个Slot包含的记录数(4-8条记录)。
记录解析
现在知道了如何通过Page Directory定位数据,就需要知道每一条记录的存储结构了, MySQL 记录格式有新旧两种(Redundant Or Compact),Index Header 中Number of Heap Records 的最高位如果是1就是Compact格式,否则是Redundant。
(storage/innobase/include/page0page.h)
1 |
不同的类型,存储结构也不相同,记录由header和data两部分组成
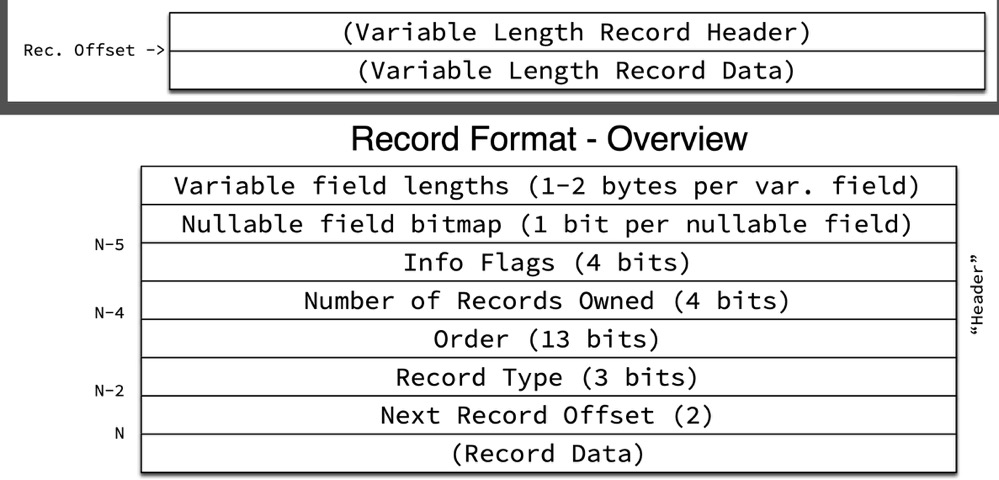
header部分存放了记录长度信息和一些额外的信息,Redundant格式为6字节,Compact格式为5字节
(storage/innobase/include/rem0rec.ic)
这里我们解析的是ibdata1文件中的系统表,其格式都是Redundant,6个字节存储的内容如下:
1 | /* Offsets of the bit-fields in an old-style record. NOTE! In the table the |
通过这些额外信息可以得到:
当前记录是否为delete记录
当前Slot中有几条记录
当前记录的类型, 如果heap number 为0是infimum,1是supremum,从2开始是用户记录
记录中有多个字段
变长字段存储格式(1 or 2 字节)
下一条记录的偏移量(相对于page)
例如我们解析第8个page,也就是innodb_sys_tables中的内容:
第8个page对应的偏移量大小是0x20000
第9个page对应的偏移量大小是0x24000

第8个page减去8个字节之后的2个字节就是第一个slot对应的值 00 65(16进制)= 101(10进制),如下图:
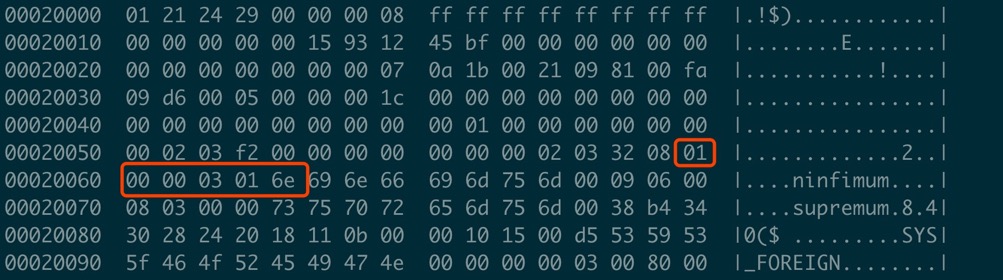
从101向前读取6字节,就是record header信息,按规则解析,解析的代码示例:
1 | h.deleteFlag = (data[0] & 0x20) != 0 |
得到值为:
| 字段 | 值 |
|---|---|
| deleteFlag | false |
| minRecFlag | false |
| Owned | 1 |
| heapNo | 0 |
| nField | 1 |
| sFlag | true |
| nextRecorder | 366 |
这可以知道记录类型是infimum, 下一条记录的Offset是366。
偏移量366对应的前6个字节内容如下:
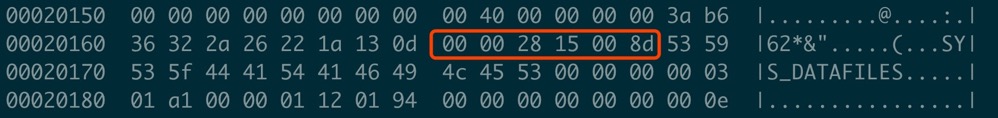
解析后的值:
| 字段 | 值 |
|---|---|
| deleteFlag | false |
| minRecFlag | false |
| Owned | 0 |
| heapNo | 5 |
| nField | 10 |
| sFlag | true |
| nextRecorder | 141 |
得到这条记录有10个字段,向前读取10个字节: 3a b6 36 32 2a 26 22 1a 13 0d, 就是字段的偏移量,通过偏移量就可以从fieldOffset位置处开始解析每一个字段的值。下面这个图更为直观一些
解析这10个字节就可以得到每个字段的长度,[13,6,7,8,4,4,8,4,0,4], 解析大致方式是判断最高位是否为1,如果不为1就取后7位,并用当前字段的解析值减去前一个字段的解析值即得到这个字段的长度,例如:
3a b6 36 32 2a 26 22 1a 13 0d
0d = 0000 1101
13 = 0001 0011
这两个字段都不为空,所以第一个字段的长度是13 , 第二个字段长度是19 - 13 = 6
通过每个字段的长度,再从fieldOffset位置处开始解析出每个字段的值:
sys_tables聚集索引的定义如下:
1 | enum dict_fld_sys_tables_enum { |
解析方法可参考函数(storage/innobase/dict/dict0load.cc)dict_sys_tables_rec_read,解析后的值:
| 字段名 | 值 |
|---|---|
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_NAME | SYS_DATAFILES |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_DB_TRX_ID | 769 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_DB_ROLL_PTR | 45317471250485761 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_ID | 14 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_N_COLS | 2 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_TYPE | 1 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_MIX_ID | 0 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_MIX_LEN | 64 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_CLUSTER_ID | null |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_SPACE | 0 |
与查询INNODB_SYS_TABLES表中的记录做个对比:

表中查询出的n_cols是5,但我们解析出来的是2,原因是表中查询会把三个隐藏字段也计算在内(DB_TRX_ID,DB_ROLL_PTR,DB_ROW_ID)。
file_format与row_format如何的出来的呢?
n_cols的第32位代表row_format格式,如果为1就是COMPACT。
file_format会比较特殊一些, 需要根据解析出来的type和n_cols共同计算完成,代码中是这样写的(storage/innobase/include/dict0dict.ic):
1 | Convert a 32 bit integer from SYS_TABLES.TYPE to dict_table_t::flags |
| 字段名 | 值 |
|---|---|
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_N_COLS | 2 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_TYPE | 1 |
n_cols为2第32位是0 , 所以redundant=1,flags的低位是0
type为1,经过与相应的标志位做’&’运算后,所有位都为0,最后的flags即是0,用一张图解释:
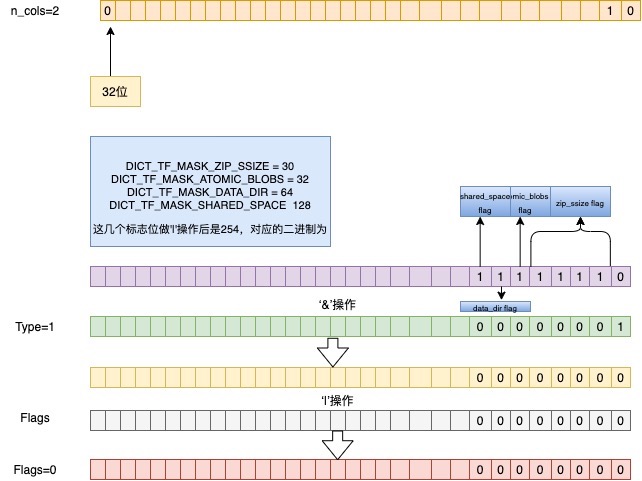
查询的时候做相应的转换,判断file_format类型:
1 | i_s_dict_fill_sys_tables( |
compact为0,!compact即为1,所以row_format为Redundant
同时atomic_blobs为0 , file_format即为Antelope
- 再用以上规则解析一条非系统表记录
| 字段名 | 值 |
|---|---|
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_NAME | dhy/dhytest2 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_DB_TRX_ID | 27446 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_DB_ROLL_PTR | 46161896180619265 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_ID | 45 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLE_N_COLS | 2147483650 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_TYPE | 33 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_MIX_ID | 0 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_MIX_LEN | 80 |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_CLUSTER_ID | null |
| DICT_FLD__SYS_TABLES_SPACE | 82 |
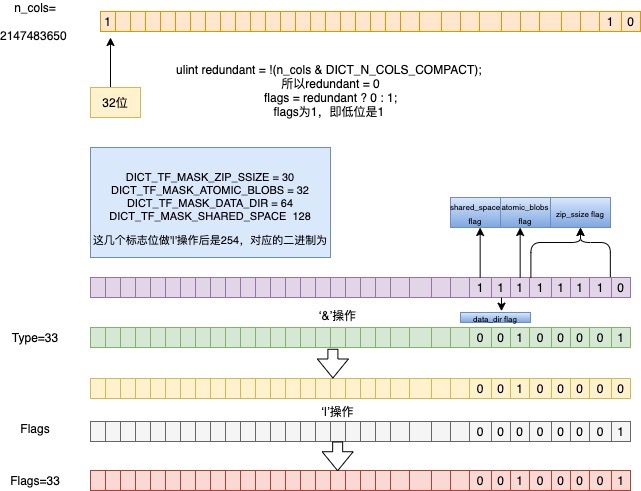
n_cols为2第32位是1 , 所以redundant=0,flags的低位是1
type为33,对应的二进制是:0010 0001,经过与相应的标志位做’&’运算后,对应的二进制为:0010 0000,在与flags做’|’操作后,二进制为:0010001,则atomic_blobs和compact为1,对应的file_format则是Barracuda, row_format是Dynamic
同时n_cols 第32位的标志位需要取消,n_cols即为2了。
与查询表中得到的信息是一致的:
<!–14–>
结语
本文介绍了Innodb系统表空间基本的结构,及如何解析ibdata表空间中的记录。通过翻阅资料和MySQL代码的查看,学习到很多技巧,例如:位移操作、逻辑运算、如何节省空间等。后面会再写一篇关于系统表加载的文章。